Working with Streaming IO
Akka Streams provides a way of handling File IO and TCP connections with Streams. While the general approach is very similar to the Actor based TCP handling using Akka IO, by using Akka Streams you are freed of having to manually react to back-pressure signals, as the library does it transparently for you.
Streaming TCP
Accepting Connections: Echo Server
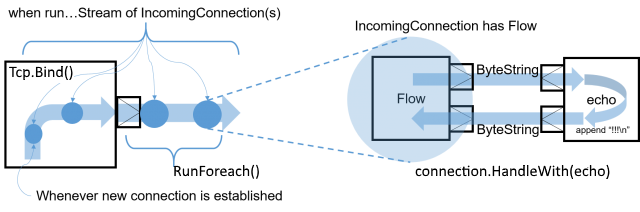
In order to implement a simple EchoServer we bind to a given address, which returns a Source<Tcp.IncomingConnection, Task<Tcp.ServerBinding>>, which will emit an IncomingConnection element for each new connection that the Server should handle:
// define an incoming request processing logic
Flow<ByteString, ByteString, NotUsed> echo = Flow.Create<ByteString>();
Tcp.ServerBinding binding = await Sys.TcpStream()
.BindAndHandle(echo, Materializer, "localhost", 9000);
Console.WriteLine($"Server listening at {binding.LocalAddress}");
// close server after everything is done
await binding.Unbind();

Next, we simply handle each incoming connection using a Flow which will be used as the processing stage to handle and emit ByteString from and to the TCP Socket. Since one ByteString does not have to necessarily correspond to exactly one line of text (the client might be sending the line in chunks) we use the Framing.Delimiter helper to chunk the inputs up into actual lines of text. The last boolean argument indicates that we require an explicit line ending even for the last message before the connection is closed. In this example we simply add exclamation marks to each incoming text message and push it through the flow:
Source<Tcp.IncomingConnection, Task<Tcp.ServerBinding>> connections =
Sys.TcpStream().Bind("127.0.0.1", 8888);
connections.RunForeach(connection =>
{
Console.WriteLine($"New connection from: {connection.RemoteAddress}");
var echo = Flow.Create<ByteString>()
.Via(Framing.Delimiter(
ByteString.FromString("\n"),
maximumFrameLength: 256,
allowTruncation: true))
.Select(c => c.ToString())
.Select(c => c + "!!!\n")
.Select(ByteString.FromString);
connection.HandleWith(echo, Materializer);
}, Materializer);
Notice that while most building blocks in Akka Streams are reusable and freely shareable, this is not the case for the incoming connection Flow, since it directly corresponds to an existing, already accepted connection its handling can only ever be materialized once.
Closing connections is possible by cancelling the incoming connection Flow from your server logic (e.g. by connecting its downstream to a Sink.Cancelled and its upstream to a Source.Empty). It is also possible to shut down the server’s socket by cancelling the IncomingConnection source connections.
var closed = Flow.FromSinkAndSource(Sink.Cancelled<ByteString>(), Source.Empty<ByteString>());
connection.HandleWith(closed, Materializer);
We can then test the TCP server by sending data to the TCP Socket using netcat (on Windows it is possible to use Linux Subsystem for Windows):
echo -n "Hello World" | netcat 127.0.0.1 8888
Hello World!!!
Connecting: REPL Client
In this example we implement a rather naive Read Evaluate Print Loop client over TCP. Let’s say we know a server has exposed a simple command line interface over TCP, and would like to interact with it using Akka Streams over TCP. To open an outgoing connection socket we use the OutgoingConnection method:
var connection = Sys.TcpStream().OutgoingConnection("127.0.0.1", serverPort);
var replParser = Flow.Create<string>().TakeWhile(c => c != "q")
.Concat(Source.Single("BYE"))
.Select(elem => ByteString.FromString($"{elem}\n"));
var repl = Flow.Create<ByteString>()
.Via(Framing.Delimiter(
ByteString.FromString("\n"),
maximumFrameLength: 256,
allowTruncation: true))
.Select(c => c.ToString())
.Select(text =>
{
Output.WriteLine($"Server: {text}");
return text;
})
.Select(_ => ReadLine("> "))
.Via(replParser);
// Client stream runs in background - completion is not awaited
// since we verify behavior via serverProbe
_ = connection.Join(repl).Run(Materializer);
The repl flow we use to handle the server interaction first prints the servers response, then awaits on input from the command line (this blocking call is used here just for the sake of simplicity) and converts it to a ByteString which is then sent over the wire to the server. Then we simply connect the TCP pipeline to this processing stage–at this point it will be materialized and start processing data once the server responds with an initial message.
A resilient REPL client would be more sophisticated than this, for example it should split out the input reading into a separate SelectAsync step and have a way to let the server write more data than one ByteString chunk at any given time, these improvements however are left as exercise for the reader.
Avoiding Deadlocks and Liveness Issues in Back-Pressured Cycles
When writing such end-to-end back-pressured systems you may sometimes end up in a situation of a loop, in which either side is waiting for the other one to start the conversation. One does not need to look far to find examples of such back-pressure loops. In the two examples shown previously, we always assumed that the side we are connecting to would start the conversation, which effectively means both sides are back-pressured and can not get the conversation started. There are multiple ways of dealing with this which are explained in depth in Graph cycles, liveness and deadlocks, however in client-server scenarios it is often the simplest to make either side simply send an initial message.
Note
In case of back-pressured cycles (which can occur even between different systems) sometimes you have to decide which of the sides has start the conversation in order to kick it off. This can often be done by injecting an initial message from one of the sides–a conversation starter.
To break this back-pressure cycle we need to inject some initial message, a “conversation starter”. First, we need to decide which side of the connection should remain passive and which active. Thankfully in most situations finding the right spot to start the conversation is rather simple, as it often is inherent to the protocol we are trying to implement using Streams. In chat-like applications, which our examples resemble, it makes sense to make the Server initiate the conversation by emitting a “hello” message:
// Use ToMaterialized to capture the binding task so we can await it
var (bindingTask, _) = Sys.TcpStream().Bind("127.0.0.1", 0) // Use port 0 for dynamic port assignment
.ToMaterialized(Sink.ForEach<Tcp.IncomingConnection>(connection =>
{
// server logic, parses incoming commands
var commandParser = Flow.Create<string>().TakeWhile(c => c != "BYE").Select(c => c + "!");
var welcomeMessage = $"Welcome to: {connection.LocalAddress}, you are: {connection.RemoteAddress}!";
var welcome = Source.Single(welcomeMessage);
var serverLogic = Flow.Create<ByteString>()
.Via(Framing.Delimiter(
ByteString.FromString("\n"),
maximumFrameLength: 256,
allowTruncation: true))
.Select(c => c.ToString())
.Select(command =>
{
serverProbe.Tell(command);
return command;
})
.Via(commandParser)
.Merge(welcome)
.Select(c => c + "\n")
.Select(ByteString.FromString);
connection.HandleWith(serverLogic, Materializer);
}), Keep.Both)
.Run(Materializer);
To emit the initial message we merge a Source with a single element, after the command processing but before the framing and transformation to ByteString this way we do not have to repeat such logic.
In this example both client and server may need to close the stream based on a parsed command - BYE in the case of the server, and q in the case of the client. This is implemented by taking from the stream until q and and concatenating a Source with a single BYE element which will then be sent after the original source completed.
Using Framing in Your Protocol
Streaming transport protocols like TCP just pass streams of bytes, and does not know what is a logical chunk of bytes from the application's point of view. Often when implementing network protocols you will want to introduce your own framing. This can be done in two ways: An end-of-frame marker, e.g. end line \n, can do framing via Framing.Delimiter. Or a length-field can be used to build a framing protocol.
Streaming File IO
Akka Streams provide simple Sources and Sinks that can work with ByteString instances to perform IO operations on files.
Streaming data from a file is as easy as creating a FileIO.FromFile given a target file, and an optional
chunkSize which determines the buffer size determined as one "element" in such stream:
var file = new FileInfo("example.csv");
var result = FileIO.FromFile(file)
.To(Sink.Ignore<ByteString>())
.Run(materializer);
Please note that these processing stages are backed by Actors and by default are configured to run on a pre-configured
threadpool-backed dispatcher dedicated for File IO. This is very important as it isolates the blocking file IO operations from the rest
of the ActorSystem allowing each dispatcher to be utilized in the most efficient way. If you want to configure a custom
dispatcher for file IO operations globally, you can do so by changing the akka.stream.blocking-io-dispatcher,
or for a specific stage by specifying a custom Dispatcher in code, like this:
FileIO.FromFile(file)
.WithAttributes(ActorAttributes.CreateDispatcher("custom-blocking-io-dispatcher"));
 Edit this page
Edit this page